

Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are stable synthetic organic compounds that were first
manufactured in the 1930's and used as refrigerants, aerosol propellants,
cleaning agents, solvents, and 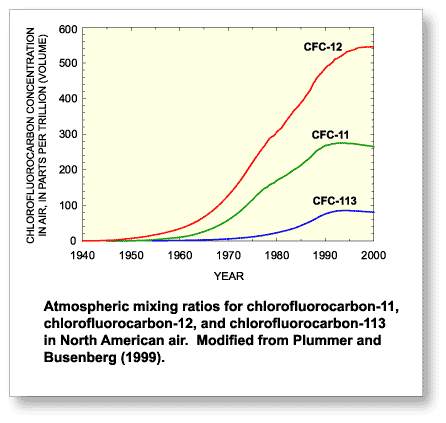 blowing agents in the
production of foam rubber and plastics (Busenberg and Plummer,
1992). CFCs are eventually released to the atmosphere and hydrosphere
and depletion of the Earth's ozone layer has been attributed to
the rapid atmospheric accumulation of these compounds (Molina
and Rowland, 1974). The method developed by Busenberg and Plummer
(1992) uses CFCs as dating tools--trichlorofluoromethane
(CCl3F, CFC-11, Freon 11), dichlorodifluoromethane
(CCl2F2, CFC-12, Freon 12), and trichlorotrifluoroethane
(C2Cl3F3, CFC-113). CFC-11
and CFC-12 make up 77 percent of total global production of CFCs
(Derra, 1990).
blowing agents in the
production of foam rubber and plastics (Busenberg and Plummer,
1992). CFCs are eventually released to the atmosphere and hydrosphere
and depletion of the Earth's ozone layer has been attributed to
the rapid atmospheric accumulation of these compounds (Molina
and Rowland, 1974). The method developed by Busenberg and Plummer
(1992) uses CFCs as dating tools--trichlorofluoromethane
(CCl3F, CFC-11, Freon 11), dichlorodifluoromethane
(CCl2F2, CFC-12, Freon 12), and trichlorotrifluoroethane
(C2Cl3F3, CFC-113). CFC-11
and CFC-12 make up 77 percent of total global production of CFCs
(Derra, 1990).
Atmospheric partial pressures of CFCs are determined by Henry's
law from the recharge temperature estimated from dissolved gases
in the sample (N2/Ar ratio) and measured concentrations
of CFCs in the ground-water samples. These calculated partial
pressures are compared with the atmospheric mixing ratios of CFCs to determine the CFC-modeled recharge date, which equates
to the time that the water was isolated from air in the unsaturated
zone.
Plummer and Busenberg (1999) state that this "clock" is set between the seasonal high and low water table. The apparent age is simply the difference between the date of sample collection and the estimated date the tracer entered the ground-water system.
Busenberg, Eurybiades, and Plummer, L.N., 1992, Use of chlorofluorocarbons (CCl3F and CCl2F2) as hydrologic tracers and age-dating tools: The alluvium and terrace system of central Oklahoma: Water Resources Research, v.28, no. 9, p. 2257-2283.
Derra, S., 1990, CFCs--No easy solutions: Research and Development, v. 32, p. 54-66.
Molina, M., and Rowland, F.S., 1974, Stratospheric sink for chlorofluoromethanes: Chlorine atom catalyzed destruction of ozone: Nature, no. 249, p. 810-812.
Plummer, L.N., and Busenberg, Eurybiades, 2000, Chlorofluorocarbons, in Cook, P.G., and Herczeg, Andrew, eds., Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology: Kluwer Academic Publishers, p. 441-478.

