

Tritium (3H) is the
radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of 12.43 years
(IAEA, 1981) and is an excellent indicator of ground water recharged
since 1952 (Clark and Fritz, 1997). 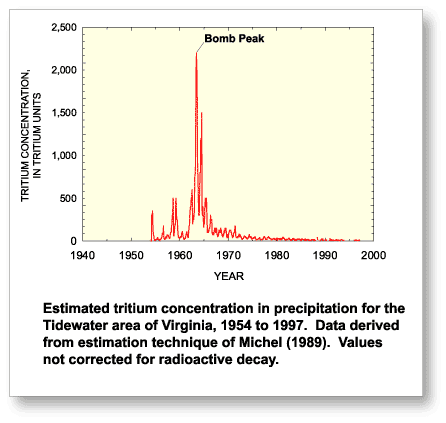 Production of 3H
in the atmosphere naturally occurs by cosmic ray spallation, but
the principal source was the atmospheric testing of thermonuclear
weapons. The standard unit of measure for 3H is a tritium
unit (TU) for which one TU is equivalent to one 3H
atom per 1018 atoms of hydrogen or in terms of radioactivity
3.2 picocuries per liter (Clark and Fritz, 1997). Tritium content
in precipitation closely mimics world events during the Cold War
years with a maximum concentration occurring in 1963, commonly
referred to as the "bomb peak". Atmospheric
concentrations have gradually declined since 1963 and present-day
ground water typically contains <1 to 10 TU, seldom exceeding
50 TU (Clark and Fritz, 1997).
Production of 3H
in the atmosphere naturally occurs by cosmic ray spallation, but
the principal source was the atmospheric testing of thermonuclear
weapons. The standard unit of measure for 3H is a tritium
unit (TU) for which one TU is equivalent to one 3H
atom per 1018 atoms of hydrogen or in terms of radioactivity
3.2 picocuries per liter (Clark and Fritz, 1997). Tritium content
in precipitation closely mimics world events during the Cold War
years with a maximum concentration occurring in 1963, commonly
referred to as the "bomb peak". Atmospheric
concentrations have gradually declined since 1963 and present-day
ground water typically contains <1 to 10 TU, seldom exceeding
50 TU (Clark and Fritz, 1997).
The tritium/helium-3 (3H/3He) method is based on the radioactive decay of 3H to 3He. Both tritium and helium are relatively inert gases. Multiple sources of 3He are present in the environment such as the Earth's mantle and atmosphere, fluid inclusions within rocks, and excess air entrained in ground water during recharge (Schlosser, 1992). This method separates 3He derived from 3H (tritogenic 3He) from 3He derived from natural sources. Apparent age estimates from the 3H/3He method can be extremely accurate (within months) for ground water containing high 3H concentrations (waters recharged since 1963). Unlike the chlorofluorocarbon dating method, 3H/3He is a valid technique for sites contaminated with organic compounds.
Clark, I.D., and Fritz, Peter, 1997, Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology: New York, Lewis Publishers, 328 p.
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), 1981, Statistical treatment of environmental isotope data in precipitation: Vienna, IAEA, Technical Report Series No. 206.
Michel, R.M., 1989, Tritium deposition in the Continental United States, 1953-1983: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 89-4072, 46p.
Schlosser, Peter, 1992, Tritium/3He dating of waters in natural systems, in Isotopes of noble gases as tracers in environmental studies: Vienna, IAEA, p. 123-145.

